China’s financing and investment spread across 61 BRI countries in 2023 (up...
2024-02-27 31 英文报告下载
Three of the top five brands in Chinese IMF are local brands, with their cumulative share doubling over five years. This illustrates the resurgence of Chinese formula manufacturers in recent years, after significant share loss after the melamine toxic milk crisis in 2008. Most of the success of the local players has until now been focused on lower-tier cities and in lower price points, but this is now beginning to change. Players like Feihe are operating more at the premium and super-premium price points and are now turning their attention to the larger coastal tier-1 and 2 cities. Other local players, such as Junlebao and Yili, are both doing well, but for now continue to focus more on the mainstream segment and on tier 3-5 cities. Danone’s Aptamil and Nestlé’s Illuma are the other two brands in the top 5, with Aptamil being the big outperformer i.e. share up four-fold since 2014. Nestlé turned its super premium brand illuma into a ‘billionaire’ brand in 2019 from virtually nothing seven years ago. Globally, Reckitt’s Enfamil is the no.1 brand given its strong position in the US (35% share) but it has been losing share in China. Abbott’s Similac is also in a similar position i.e. no.2 in US IMF with a >30% share but much less strong in China. Both these brands have suffered from a lack of exposure to the super-premium segment, in our view. The other notable brands in the global top 10 are Friesland Campina’s Friso (5% share in China) and Nestlé’s Nan brand.
There are other structural headwinds to population growth in China. The number of women aged 25-35 (key child bearing age) will decrease by c.40 million in the next 10 years and the implementation of the two-child policy has not had the desired impact. In addition, the cost of raising a child is significantly higher in China – buying premium formula every month for a 2– 3-month-old baby can cost up to c.40% of monthly salary. If there is another down year in terms of births, which we think is likely in 2020, we would not be surprised if the government takes action. Better maternity benefits would be an obvious area. New regulation introduced in 2018 to address food safety issues has consolidated the market and local manufacturers seem to be gaining traction. The market share of the two biggest Chinese IMF companies, Feihe and Jun Le Bao, has doubled in the last two years while that of Nestle, Danone, Reckitt and Abbott combined has flat-lined. In June’19, the government announced a target to reach 60% self-sufficiency within three years i.e. 60% of total IMF consumption manufactured locally by 2022. This comes at a time when lower-tier cities, where domestic companies have a strong position, are outperforming. Companies are now looking at growth opportunities in lower tier cities – Birth rates in tier 4 cities and below is almost twice that of the rest of the country. While distribution is a key challenge for multinationals, the main question is if they have the right portfolio and go-to market strategy to succeed in tier 3/4/5 cities. We think this will be an uphill battle and is likely to take a year or two for multinationals to find the right product at the right price point to deliver on local consumer preferences. Lower-tier cities need a unique marketing model to drive awareness and penetration. As consumers in lower-tier cities are less likely to fully comprehend the science behind IMF (infant milk formula) products, educating them and developing brand awareness is crucial. For example, Feihe held more than 500,000 face-to-face seminars with Chinese mothers, educating them about the advantages of its products. Interestingly, with increased trust in the category, safety has become less of a concern and the focus is now back on product superiority and functional benefits, making innovation crucial.

标签: 英文报告下载
相关文章
China’s financing and investment spread across 61 BRI countries in 2023 (up...
2024-02-27 31 英文报告下载

Though the risk of AI leading to catastrophe or human extinction had...
2024-02-26 52 英文报告下载
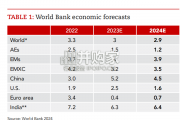
Focusing on the prospects for 2024, global growth is likely to come i...
2024-02-21 96 英文报告下载

Economic activity declined slightly on average, employment was roughly flat...
2024-02-07 67 英文报告下载
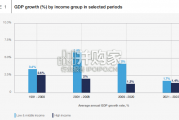
Economic growth can be defned as an increase in the quantity or quali...
2024-02-06 82 英文报告下载
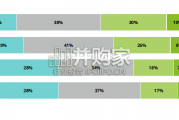
In this initial quarterly survey, 41% of leaders reported their organizatio...
2024-02-05 66 英文报告下载
最新留言