China’s financing and investment spread across 61 BRI countries in 2023 (up...
2024-02-27 32 英文报告下载
Artifificial intelligence (AI): A broad discipline with the goal of creating intelligent machines, as opposed to the natural intelligence that is demonstrated by humans and animals. It has become a somewhat catch all term that nonetheless captures the long term ambition of the fifield to build machines that emulate and then exceed the full range of human cognition. Machine learning (ML): A subset of AI that often uses statistical techniques to give machines the ability to "learn" from data without being explicitly given the instructions for how to do so. This process is known as “training” a “model” using a learning “algorithm” that progressively improves model performance on a specifific task. Reinforcement learning (RL): An area of ML that has received lots of attention from researchers over the past decade. It is concerned with software agents that learn goal-oriented behavior by trial and error in an environment that provides rewards or penalties in response to the agent’s actions (called a “policy”) towards achieving that goal. Deep learning (DL): An area of ML that attempts to mimic the activity in layers of neurons in the brain to learn how to recognise complex patterns in data. The “deep” in deep learning refers to the large number of layers of neurons in contemporary ML models that help to learn rich representations of data to achieve better performance gains.
Algorithm: An unambiguous specifification of how to solve a particular problem. Model: Once a ML algorithm has been trained on data, the output of the process is known as the model. This can then be used to make predictions. Supervised learning: This is the most common kind of (commercial) ML algorithm today where the system is presented with labelled examples to explicitly learn from. Unsupervised learning: In contrast to supervised learning, the ML algorithm has to infer the inherent structure of the data that is not annotated with labels. Transfer learning: This is an area of research in ML that focuses on storing knowledge gained in one problem and applying it to a different or related problem, thereby reducing the need for additional training data and compute. Natural language processing (NLP): Enables machines to analyse, understand and manipulate textual data. Computer vision: Enabling machines to analyse, understand and manipulate images and video.

标签: 英文报告下载
相关文章
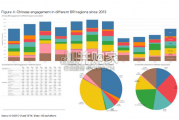
China’s financing and investment spread across 61 BRI countries in 2023 (up...
2024-02-27 32 英文报告下载

Though the risk of AI leading to catastrophe or human extinction had...
2024-02-26 53 英文报告下载
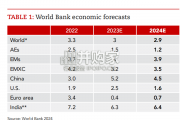
Focusing on the prospects for 2024, global growth is likely to come i...
2024-02-21 99 英文报告下载

Economic activity declined slightly on average, employment was roughly flat...
2024-02-07 68 英文报告下载
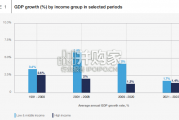
Economic growth can be defned as an increase in the quantity or quali...
2024-02-06 82 英文报告下载
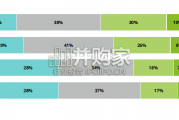
In this initial quarterly survey, 41% of leaders reported their organizatio...
2024-02-05 66 英文报告下载
最新留言